
What is JPG to Excel OCR? Everything You Need to Know
You receive a client email with a table screenshot attached. "Can you add this data to our system by tomorrow?" they ask. Your heart sinks—retyping 50 rows of numbers sounds like a nightmare.
This is exactly why people search for JPG to Excel OCR solutions. OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology promises to extract text from images automatically, saving hours of manual data entry. But how well does it actually work for converting table images to Excel spreadsheets?
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore what OCR technology is, how it handles JPG to Excel conversion, its real-world capabilities, and—importantly—where it struggles. Understanding both the strengths and limitations will help you choose the right approach for your specific needs.
What is OCR Technology?
OCR stands for Optical Character Recognition—a technology that converts different types of documents (scanned paper documents, PDF files, or images captured by a digital camera) into editable and searchable data.
The concept dates back to the 1950s when early OCR machines could recognize one font at a time. According to Wikipedia's OCR article, modern OCR has evolved dramatically. Today's systems can handle multiple fonts, languages, and even handwriting to varying degrees.
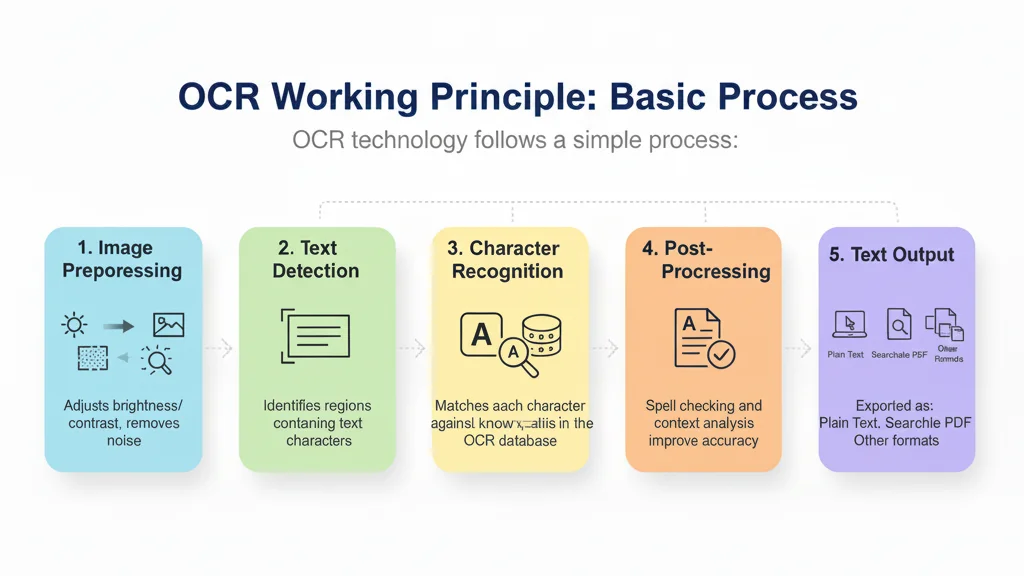
How OCR Works: The Basic Process
OCR technology follows a straightforward pipeline:
- Image Preprocessing: The system adjusts brightness, contrast, and removes noise from the image
- Text Detection: Algorithms identify regions containing text characters
- Character Recognition: Each character is matched against known patterns in the OCR database
- Post-processing: Spell-checking and context analysis improve accuracy
- Text Output: The recognized text is exported as plain text, searchable PDF, or other formats
Think of OCR like a person reading a book aloud—they look at each letter, recognize it, and speak it out. The technology is excellent at this fundamental task: turning printed or typed text into digital characters.
How JPG to Excel OCR Works
When you specifically want to convert JPG to Excel using OCR, the process becomes more complex than simple text extraction. The system needs to:
Step 1: Image Quality Assessment
The OCR tool analyzes your JPG image quality. Issues like low resolution (below 300 DPI), poor lighting, or camera angle distortions are flagged because they significantly impact accuracy.
Step 2: Text Recognition
The OCR engine scans the image and extracts all visible text. Popular engines include:
- Google Cloud Vision API - Known for high accuracy across multiple languages
- Tesseract OCR - Open-source and free, widely used in free OCR JPG to Excel tools
- Azure Computer Vision - Microsoft's enterprise solution with strong table detection
- Amazon Textract - AWS service specifically designed for document and table extraction
Step 3: Text Structuring (The Critical Challenge)
Here's where JPG to Excel OCR faces its biggest hurdle. The OCR output is essentially a list of text strings with positional coordinates. The system attempts to:
- Group text into rows based on vertical alignment
- Identify columns based on horizontal spacing
- Detect table borders or gridlines as structural guides
- Create a matrix structure suitable for Excel
Step 4: Excel File Generation
Finally, the structured data is written into an Excel file format (.xlsx or .csv), with each detected cell assigned to a row and column position.
Many ocr online JPG to Excel services automate this entire workflow through a web interface, requiring just a file upload and a download click.
The Advantages of Using OCR for JPG to Excel Conversion
Despite limitations we'll discuss shortly, traditional OCR has legitimate strengths that make it valuable in specific scenarios:
1. Mature and Widely Available Technology
OCR has been refined over decades. This means:
- Extensive documentation and community support
- Integration with many business software platforms
- Predictable performance characteristics
2. Abundant Free Options
Searching for free OCR JPG to Excel tools yields dozens of results. Open-source projects like Tesseract can be self-hosted at zero cost, making OCR accessible for individuals and small businesses with tight budgets.
3. Fast Processing for Simple Documents
For straightforward tables—think basic spreadsheets with clear borders and uniform fonts—OCR performs quickly. A single-page invoice or receipt can be processed in seconds.
4. No Training Required
Unlike machine learning models that need training data, rule-based OCR systems work out of the box. Upload an image, get text output—no configuration needed for basic use cases.
5. Works Completely Offline
Desktop OCR software can run without internet connectivity, which is crucial for organizations handling sensitive financial or medical data that cannot be uploaded to cloud services.
The Limitations of OCR Technology for Table Recognition
Now we arrive at the critical part: understanding what OCR cannot do well. These limitations aren't theoretical—they're daily frustrations for people trying to convert table images to Excel.
1. OCR Only Extracts Text, Not Table Structure
This is the fundamental limitation. OCR sees your table as a collection of text snippets, not as a structured data grid.
What this means in practice:
- OCR identifies the text "Q1 Revenue" but doesn't understand it's a column header
- It sees "12,450" but doesn't know which row and column it belongs to
- Relationships between cells are guessed based on spacing, not understood semantically
Research published in the International Journal on Document Analysis and Recognition shows that while modern OCR achieves 95%+ accuracy for character recognition, table structure extraction accuracy drops to 60-75% for moderately complex tables.
2. Merged Cells Cause Complete Confusion
Excel users regularly merge cells for headers or labels. OCR has no concept of merged cells.
Real-world example: Imagine a table where "Department Budget - Q1 2024" spans three columns as a merged header. OCR might:
- Place the entire text in the first column
- Split it randomly across all three columns
- Lose alignment with the data rows below
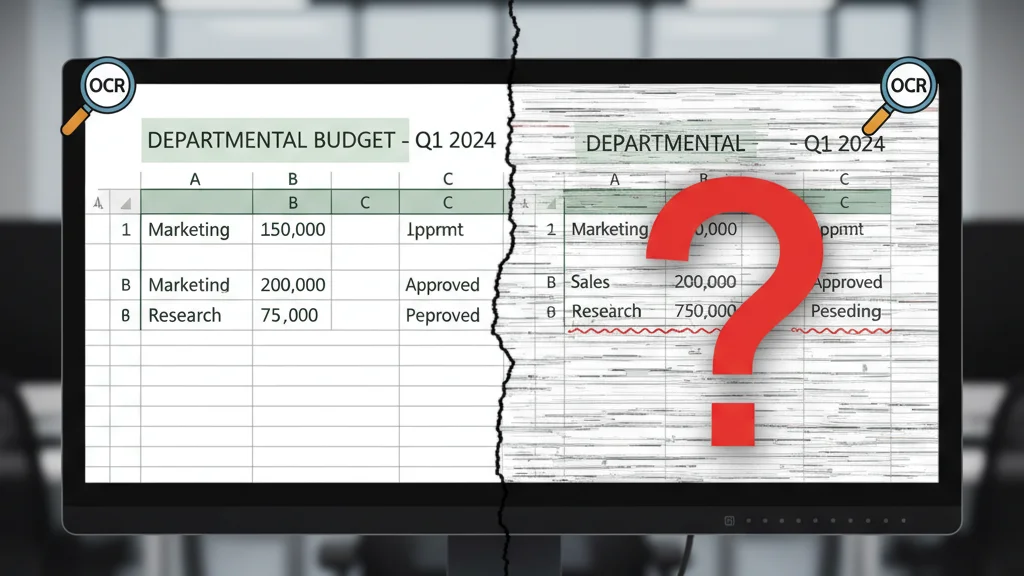
According to studies on document digitization from Adobe Research, merged cell recognition remains one of the top failure points in table extraction, with error rates exceeding 40%.
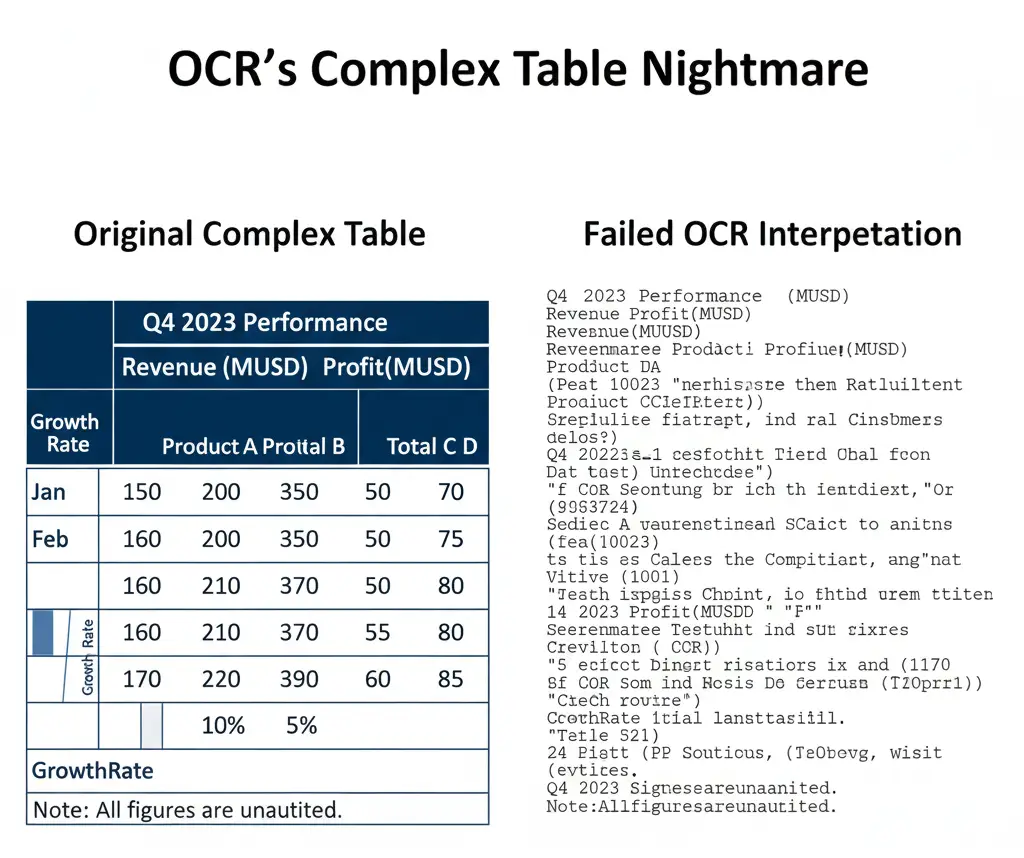
3. Complex Table Layouts Break Down
Multi-level headers, nested tables, diagonal split cells—these common table features are OCR's nightmare.
Elements that confuse traditional OCR:
- Multi-level headers: A header row that groups several sub-headers beneath it
- Irregular column widths: OCR might merge narrow columns or split wide ones incorrectly
- Rotated text: Vertical or diagonal text in cells often goes unrecognized
- Borderless tables: Without clear gridlines, OCR struggles to detect column boundaries
4. Image Quality Issues Lead to Errors
OCR demands high-quality source images. Real-world photos rarely meet this standard.
Common image problems:
- Blur or low resolution: Characters become ambiguous (is that "8" or "B"?)
- Skewed angles: Photos taken at an angle distort character shapes
- Shadows and glare: Uneven lighting causes some areas to be unreadable
- Wrinkled or folded paper: Physical distortions in the original document
- Handwritten annotations: Most OCR systems cannot reliably read handwriting
Research from Microsoft on OCR accuracy found that a 15-degree camera angle can reduce accuracy by up to 25%, and poor lighting conditions can drop it by 30-40%.
5. Extensive Manual Correction Required
Even when OCR successfully processes a table, you're rarely done.
Time spent on post-OCR editing:
- Correcting misread characters (common: "1" read as "I", "0" as "O")
- Realigning misplaced data into correct columns
- Reconstructing merged cells manually
- Fixing formatting (bold, colors, cell borders are completely lost)
- Validating numbers (a critical step for financial data)
User feedback from productivity forums suggests that for a 20-row table with moderate complexity, OCR saves the initial typing but requires 10-15 minutes of correction work—sometimes taking longer than manual entry would have.
6. Inconsistent Results Across Different Engines
Not all OCR engines perform equally. The same table image processed through different OCR online JPG to Excel services can yield dramatically different results.
Variables affecting performance:
- Training data used (some engines excel with English but struggle with numbers)
- Algorithm approach (template matching vs. neural network-based)
- Processing parameters (confidence thresholds for character recognition)
- Cost tier (premium API versions usually outperform free tiers)
This inconsistency means you often need to try multiple tools to find acceptable results.
How to Choose the Right JPG to Excel OCR Tool
Given these limitations, selecting an appropriate tool requires careful evaluation. Here's a practical framework:
For Simple, Clean Tables:
If your tables have:
- Clear borders and gridlines
- Uniform fonts and sizes
- No merged cells or complex layouts
- High-resolution source images
Recommended approach:
- Start with free OCR JPG to Excel online tools
- Tesseract-based open-source solutions work well
- Expect 80-90% accuracy with minimal editing needed
For Complex or Irregular Tables:
If your tables include:
- Merged cells or multi-level headers
- Mixed formatting (different fonts, sizes, colors)
- Borderless or partially bordered layouts
- Photos with imperfect angles or lighting
Recommended approach:
- Premium OCR services with table-specific training (like Adobe Acrobat Pro or ABBYY FineReader)
- Be prepared for significant manual correction
- Consider whether AI-powered alternatives might be more efficient
Free vs. Paid OCR Tools
Free options (Tesseract, Google Keep OCR, free online converters):
- ✅ Zero cost, unlimited personal use
- ✅ Sufficient for occasional, simple conversions
- ❌ Limited accuracy on complex documents
- ❌ Often have file size or volume restrictions
- ❌ Minimal customer support
Paid solutions ($10-50/month typically):
- ✅ Higher accuracy rates (typically 5-15% better)
- ✅ Better handling of poor-quality images
- ✅ Batch processing capabilities
- ✅ Customer support and regular updates
- ❌ Ongoing subscription costs
Practical Tips to Improve OCR Accuracy
If you're committed to using OCR for JPG to Excel conversion, these techniques will significantly improve results:
Before Taking the Photo or Scanning:
- Maximize resolution: Use at least 300 DPI for scans, 12+ megapixel cameras for photos
- Ensure even lighting: Avoid shadows and glare; natural indirect light works best
- Photograph straight-on: Position the camera directly above the document, parallel to the page
- Clean the document: Remove any marks, stains, or background clutter
- Use a plain background: Place documents on a solid, contrasting background color
Image Preprocessing (Before OCR):
- Convert to grayscale: Color information doesn't help OCR and increases processing time
- Increase contrast: Make text darker and background lighter
- Apply sharpening: Slightly sharpen edges for clearer character definition
- Crop tightly: Remove margins and non-table content
- Rotate to correct orientation: Ensure text is perfectly horizontal
Free tools like GIMP, Photoshop, or even simple preview apps can handle these adjustments.
During OCR Processing:
- Choose the correct language: Many OCR tools perform better when you specify the document language
- Use table-specific modes: Some OCR software has a dedicated "table detection" mode
- Try multiple engines: Don't accept the first result—test 2-3 different OCR tools
- Process sections separately: For large tables, divide into smaller sections for better accuracy
After OCR Output:
- Always validate numbers: Double-check financial figures and calculations
- Cross-reference totals: If the original has sum rows, verify they match
- Check date formats: OCR often misinterprets date formats
- Review special characters: Currency symbols, percentages, and mathematical operators need verification
Frequently Asked Questions
Is OCR free for JPG to Excel conversion?
Yes, several free options exist. Tesseract OCR is open-source and completely free. Google Docs has built-in OCR (upload an image, it extracts text). Many websites offer free OCR JPG to Excel online services with limitations—typically capped at 15-20 pages per hour or with file size restrictions. For high-volume or commercial use, paid solutions offer better accuracy and support.
Can OCR achieve 100% accuracy for table recognition?
No. Even the best OCR systems typically achieve 85-95% character-level accuracy for simple, clean tables. Complex tables with merged cells, multi-level headers, or poor image quality can drop accuracy below 70%. According to the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) benchmarks, perfect table structure recognition remains an unsolved challenge in document analysis.
When should I NOT use OCR for JPG to Excel?
Avoid OCR when:
- Tables have extensive merged cells or nested structures
- Source images are blurry, skewed, or low-resolution
- Data is handwritten or in unusual fonts
- Accuracy is critical (financial statements, legal documents) and you lack time for thorough verification
- You need to preserve formatting (colors, fonts, cell styles)
In these cases, manual entry or AI-powered recognition tools may be more efficient.
What's the difference between OCR and AI recognition?
Traditional OCR uses pattern matching and rules to identify characters—essentially asking "does this shape match the letter A in my database?" Modern AI-powered recognition uses deep learning neural networks to understand context, table semantics, and relationships between cells. AI can infer that a cell is a header based on position and formatting, not just coordinate proximity. This fundamental difference is why AI-based tools can handle merged cells and complex layouts that break traditional OCR.
The Bottom Line: OCR's Role in Table Extraction
OCR technology for JPG to Excel conversion is a valuable tool—but it's not magic. Its character recognition capabilities are impressive, especially for clean, simple documents. However, when it comes to understanding and preserving table structure, traditional OCR shows its age.
OCR works well when:
- You have high-quality images of simple tables
- Minor errors are acceptable and fixable
- Budget is limited (free tools available)
- Tables have clear borders and uniform formatting
OCR struggles when:
- Tables use merged cells or complex layouts
- Image quality is poor or documents are photographed at angles
- You need high accuracy with minimal manual correction
- Formatting and structure must be preserved perfectly
As document digitization becomes more critical for businesses, the limitations of rule-based OCR have driven innovation toward newer approaches. Machine learning and AI-powered recognition systems are beginning to address OCR's structural blindness, offering promising alternatives for complex table extraction tasks.
Understanding what convert JPG to Excel OCR technology can and cannot do empowers you to make informed decisions about your document workflow. Sometimes OCR is the perfect tool. Other times, investing in more advanced solutions—or even careful manual entry—delivers better results faster.
Ready to convert your table images to Excel? Try different OCR tools with a sample image first. Compare the results, note the error patterns, and choose the approach that fits your accuracy requirements and budget.
Last updated: November 14, 2025
Have questions about table extraction technology? Check out our other guides on image-to-Excel conversion.
Author

Categories
More Posts

How to Bulk Convert Multiple Table Images to Excel in One Click
Stop typing table data one by one! This comprehensive guide shows how to use AI-powered technology to bulk convert multiple table images to Excel files online, with support for merged cells and automatic table structure recognition—boosting efficiency by 5-20x.


How AI Transforms JPG to Excel Conversion: A Deep Dive into jpg to excel converter ai
Discover how AI-powered JPG to Excel converters outperform traditional OCR. Learn why deep learning technology achieves 95%+ accuracy on complex tables with merged cells, multi-level headers, and real-world image quality issues.

How to Convert Image to Excel in Seconds
Stop retyping table data by hand—this step-by-step image to Excel tutorial shows how to turn JPG, PNG, or scanned tables into editable Excel spreadsheets in under 10 seconds.
